All fountain pens require liquid ink, so an important part of selecting a fountain pen is determining which mechanism of filling and containing ink you would prefer. There are three major types of ink-filling systems: cartridges, converters, and built-in mechanisms. These three systems vary in price, convenience, durability, and have a large impact on your experience with your instrument.
Cartridge
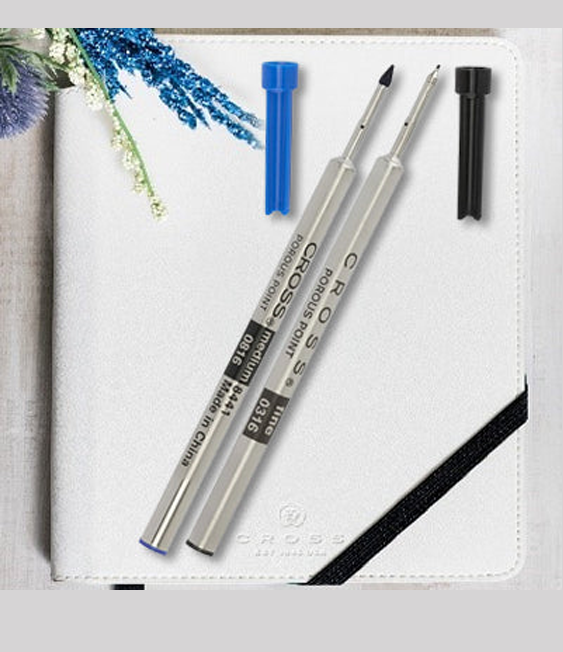
One of the most popular ink reservoir mechanisms, cartridges allow their user to easily handle and insert ink into their pen in small quantities. A cartridge is a sealed and pre-filled tube of ink that is functionally "popped" open when insert into your pen to release ink. Cartridges are the least expensive of the three ink-filling systems, and also make handling and replacing ink faster and mess-free by simply taking one cartridge out and putting a new one in.
A notable downside to using cartridges is that certain pen brands are only compatible with cartridges made by the same brand. Secondly, a cartridge of ink typically contains less ink than a pen with a built-in system, so your cartridges may need to be replaced more often. Cartridges also have a more limited selection of inks and require their user to opt out of the world of bottled inks, which can have unique color values, dual-hues, or even shimmer qualities.
Cartridge Converter
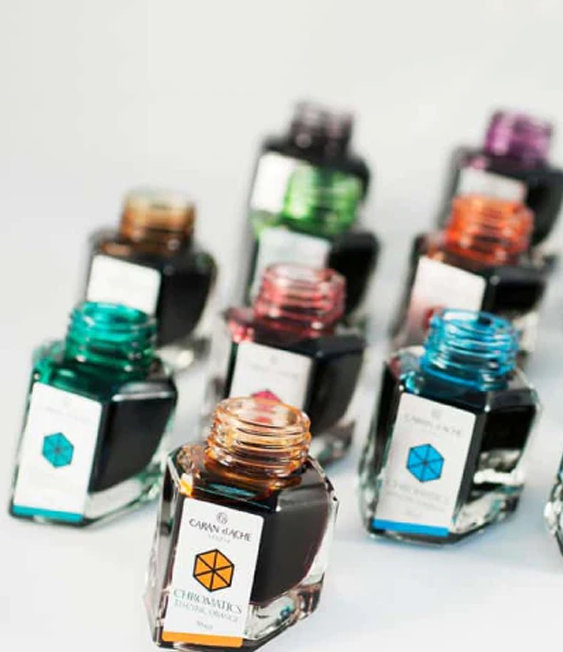
Converters are clear plastic tubes that the user fills with ink from a bottle. In most fountain pens, you dip the pen nib in the bottle of ink, and then squeeze or twist the converter to draw ink upwards into the cartridge. Many cartridge fountain pens are compatible with converters. Using a converter opens the user to a large variety of bottled inks rather than just being limited to proprietary cartridges.
Built-In Filling System
Lastly, some pens (TWSBI pens are an excellent example because they utilize a vacuum-mechanized reservoir) are crafted with ink reservoirs as a part of their design and therefore do not require cartridges or converters. Functionally, this means you can fill your pen straight from the bottle. Similarly to a converter, built-in ink-filling systems require you to dip the nib of the pen into a bottle of ink and then usually twist a knob (although every brand is different and may use different mechanisms than a twisting mechanism) to work the ink upwards. Some pens also come with a vacuum-based system when a plunger on the pen is used to collect the ink. Pens with built-in filling allow you to work with a large variety of bottled inks and will tend to have larger ink capacity than other ink-filling systems, but may come at a higher price point or require more maintenance.
If you are unsure which cartridge or converter is right for your fountain pen, feel free to consult our Library page on our website, which contains helpful information about the refill compatibility of the brands we offer!